Data hosting guide:
Styling, search, reports & more
Your data’s now on Ratio.City. So, what can you do with it?
Leverage your data to unlock new insights: create data visualizations with our styling tools, cross-reference your data against our extensive data catalog, and more—see your data in a whole new light with Ratio.City.
Pssst. If you’re looking for how to upload your data, go here instead.
Data styling & visualization
The data styling interface can be found in the secondary panel; click on any layer in the layer list to open it
You can edit and save the styling for all your company layers; any styling that you save will be visible to all users from your organization
Any changes you make to the other layers in the layer list (that were not uploaded by your organization) will only persist for your current session
00:00 Intro
00:07 Styling interface & simple styling
01:11 Data-driven styling: Text-based fields
02:05 Data-driven styling: Numeric fields
02:35 Saving your work
For polygon layers, you will be able to adjust opacity and fill
For line layers, you can adjust the opacity and the colour and width of the lines (there is no ‘fill’ property in a line layer)
For point layers, you can adjust the opacity and the line colour around the circle as well as the actual circle
Some layers have data fields that can be displayed either with a fixed fill (all the same colour) or data-driven fill
You can pick the data field you want to use to visualize your dataset; different styling options are available depending on the data type of your chosen field (which you would have set up in Step 3 of the upload process)
Numerical data types (integers or decimals): you’ll be able to select a colour gradient that applies on a scale based on the range of numerical values in your dataset for that field
Text data types (string or boolean): each value will have a colour associated and you can either apply a default colour scale from the dropdown or individually pick colours for each class by clicking on the coloured square next to the class name
The automatic colour scale styling will only apply to the first 12 classes of whichever data field you pick
If you want to include more than 12, you can add the classes using ‘Add Class’ at the bottom of the classes list
You can remove classes with the ‘x’ and they will change to the default colour
You can adjust the styling for all the layers you have access to, but you will only be able to save your changes for layers that you’ve uploaded
Saved changes will be visible to all users within your organization
Changes you make to Ratio.City layers will persist only for the duration of your session
Search & filter data in Locate mode
You’ll find your layers in the dropdown menu in Locate mode under the ‘My Layers’ section; select the layer you want to search with
The layer will only appear in the dropdown if it’s within your map view, so if you can’t find it, check that your map is showing the right area
We are working on an updated version of this video. Thank you for your patience! [July 2022]
00:00 Intro
00:20 Filtering within your datasets
01:54 Filtering against other datasets
02:00 Parcel layers
02:25 Non-parcel layers
Filtering within your datasets
Once selected, you’ll be able to filter by almost any of the data fields you’ve imported when you uploaded the dataset. This is available for any line, point, and polygon layers that you’ve uploaded.
Text-based data fields—anything that is a string or boolean data type—can be filtered using the ‘equals to’ or ‘not equals to’ operators as long as they have between 2 and 100 different values within the dataset and if the field is not a URL
If your data field has more than 100 unique text fields, it will not show up as an option in the dropdown.
Numeric data fields (integers and decimals) can be used with the ‘less than’, ‘greater than’, or ‘between’ operators
If you’re filtering a numerical field and want to filter for just one specific value, you can use the ‘between’ operator and input the same value for the upper and lower inputs. For example, between 2 <> 2.
Filtering against other datasets
If your layer is a point or polygon layer, you’ll be able to filter your data against other datasets
The available datasets will appear in the filter dropdown after you’ve selected your layer
With these filters, you can see if your parcels overlap with specific zoning categories, are adjacent to Right-of-Ways, whether there are surrounding transit stops, and more—use Locate mode to gain insights about your data
Getting intersecting parcel data for your custom layer
If you have uploaded a point or polygon layer and want to see the parcels that your layer intersects with, you can select the parcel layer of the city you’re searching in (eg. Toronto Parcels) and then add your data layer as a filter
The search results will show you the details of the parcels that intersect or contain the data points from your custom layer, including the parcel area, existing coverage, and existing FAR
You can filter against other Ratio.City layers within the same search
If you’d like more information on Locate mode in general, check out our full video tutorial.
Capture your data in a report
You can select one or more points and click ‘Get Details’ to get the full site details and report based on your point selection
To get full site details and reports on polygon layers, simply select one or more polygons and use them to create a site
Generating reports directly from line layers is not available at this time—if this is something you’re interested in, please reach out to us. We’d love to see how we can help
Data management
You can view the full list of your organization’s datasets in the data section
Please note that all changes made here affect every user within your organization
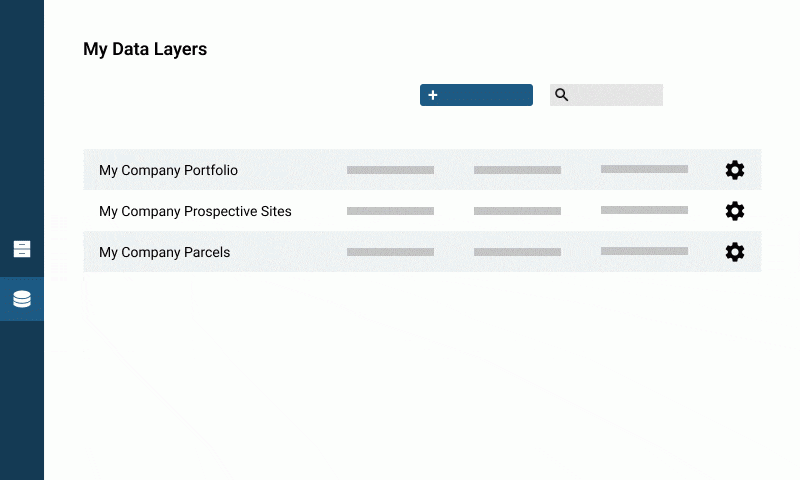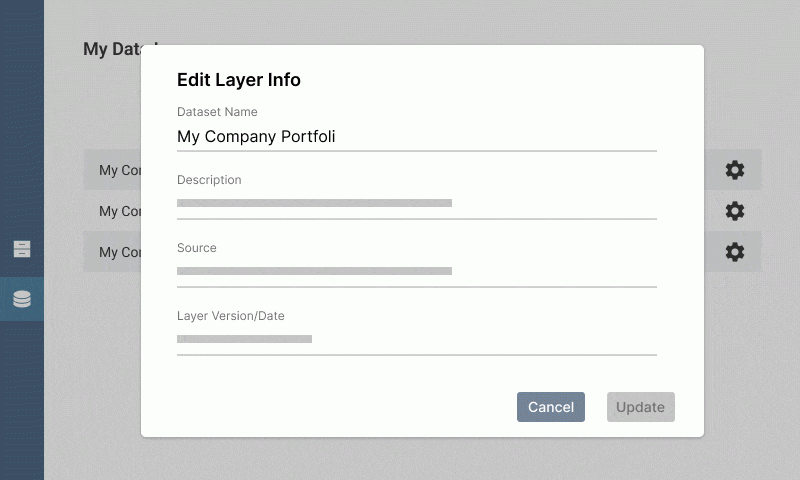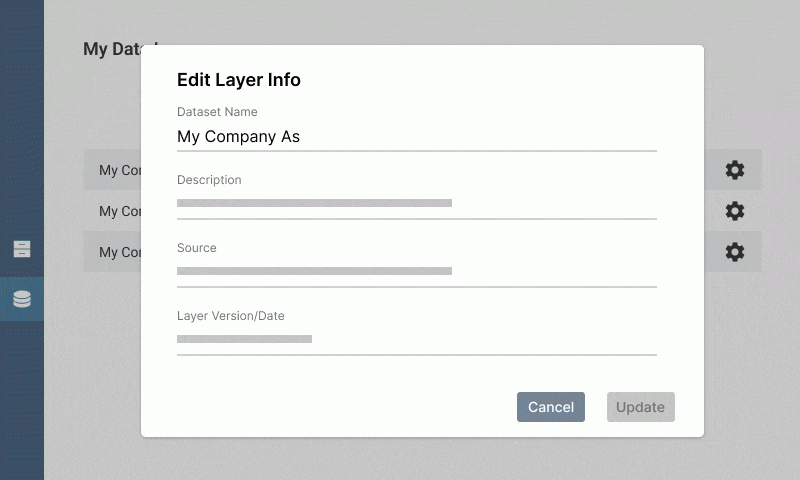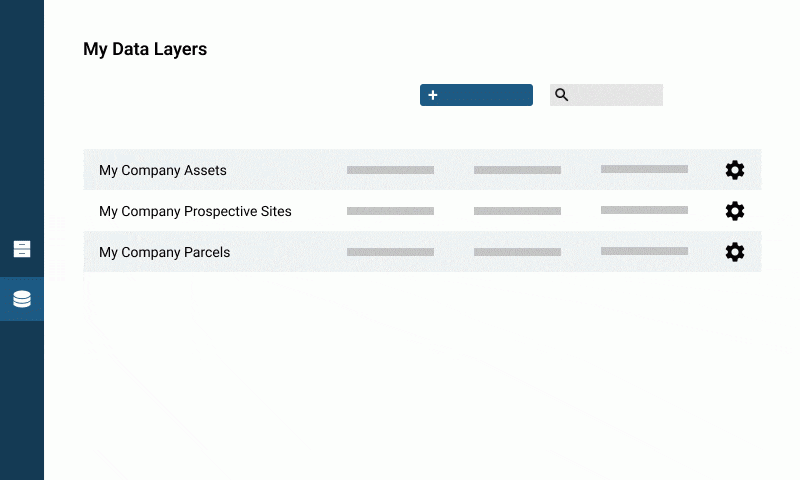
Edit layer information
Click the layer to access the menu: you can edit the dataset name, description, source, source URL, and version date from here
Archiving & deleting datasets
Click the layer to access the menu to archive and delete datasets
Archiving a dataset will cause it to disappear from the layer list in Explore and Locate mode, but you will still be able to see it in the data section and unarchive it if you wish to do so
Deleting a dataset is permanent and cannot be undone. It’s probably safer to archive the dataset rather than deleting it unless you’re very sure you won’t need it again
Archiving or deleting a dataset will affect all users in your organization
Replacing a layer
Before you start
Prep your file following our Data & Formatting Guidelines
There are two ways to enter the layer replacement workflow:
From the Data section: click on the cog icon to access the menu and select ‘Replace’
From the data upload interface: click the checkbox for ‘Replace an existing dataset’ and select the dataset you want to replace from the dropdown
Step 1: Upload new your file
To replace a layer, upload your file as normal and proceed to Step 2
Step 2: Enter/update dataset details
Your dataset details will be automatically populated based on what you input when the previous version of the dataset was uploaded
Update the form fields if there have been changes from your previous upload (eg. a new last modified date or description)
Step 3: Review & update any data fields
00:00 Intro
00:30 No changes in dataset field names
00:45 Changes detected: Update your dataset fields
01:31 Additional dataset fields
01:50 Review & confirm changes
Similarly, the data you imported in the previous version of the dataset will be automatically populated if the names of your dataset fields remain the same. You can review and make changes to the labels if needed
If there are changes to any of the dataset fields that you previously imported, you will find them in the second section and be asked to update the fields to match labels that you had in the previous version
For example, if you’ve changed a field previously called ‘height’ to ‘building height’
You can choose not to import these fields if they are no longer relevant. Simply uncheck the checkbox for ‘Imported’
Lastly, you can import any of the other dataset fields that remain. This step is optional and incomplete fields will not be imported
Step 4: Review & confirm your changes
When replacing a layer, you can choose to change the main label if you want
Note that if the previous field you were using as the main label was removed in Step 3, the platform will default to using your first imported field by alphabetical order
Once you’re happy with the main label, click ‘Create Layer’ to complete the upload process
Once you’ve completed the upload of your replacement layer, the previous version of the layer will be automatically archived. You can still view the previous version in the data section
Replaced layers will appear with the default Ratio.City styling, so if you want to customize how they look, you’ll have to do so when the upload is complete and save the new styling
Still have questions?
Contact our team at data@ratio.city. We’re happy to help!